Our Projects
6 cylinder, v type, 4000 cc Engine crankshaft prototyping for the first time in Iran
From material selection to dynamic balancing and quality control, this project showcases our full-spectrum capabilities in crankshaft localization and production.
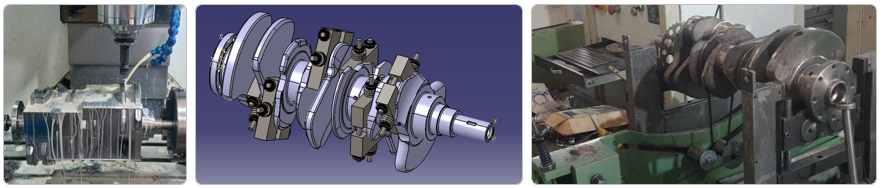
Introduction
The crankshaft, often described as the beating heart of internal combustion engines, plays a crucial role in converting the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion to transmit power to the drivetrain. This complex component, crafted from high-strength alloys, is manufactured with precision engineering and advanced technologies to ensure strength, durability, and optimal performance in vehicles and industrial machinery.
Material Selection
The selection of raw materials for the crankshaft is critical due to its exposure to high stresses, cyclic loads, and mechanical fatigue. Typically, high-strength steel alloys, such as chrome-molybdenum steel, are used for their excellent tensile strength and fatigue resistance. For more cost-effective applications, such as light-duty vehicle engines, nodular cast iron is chosen for its adequate wear resistance and lower cost. We take the first step toward ensuring product quality and performance by meticulously selecting the most comparable and optimal material substitute in terms of performance and mechanical properties, tailored to the original crankshaft specifications and compatible with the manufacturing processes.
Redesign and Manufacturing
The manufacturing process begins with precise design using CAD software like CATIA or SolidWorks, where a refined 3D model is developed from point cloud data obtained via scanning, and detailed engineering drawings are created with specified tolerances and Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) standards. Based on supply chain management and customer requirements, the initial shaping process is selected from forging, casting, or billet machining. High-quality raw material sourcing and coordination with suppliers are essential to avoid production delays. Customer requirements, such as performance specifications (e.g., torque or power output), industry standards, and cost constraints, influence the choice of materials and manufacturing methods. After initial shaping, the crankshaft undergoes precise machining to achieve final dimensions and smooth surfaces. CNC machines are employed for turning and grinding main journals, crankpins, and contact surfaces to meet tight tolerances (in the micron range) and GD&T standards. Additionally, oil passages are drilled to facilitate lubrication to the bearings, which is crucial for reducing friction and extending component life. Counterweights are also machined to minimize vibrations, ensuring smooth engine operation. To increase hardness and wear resistance, the crankshaft undergoes heat treatment processes such as induction hardening or nitriding. These processes elevate the surface hardness of main and connecting rod journals to 50–60 HRC, while maintaining the core’s ductility to withstand dynamic stresses, ensuring durability under high-load conditions.
Balancing
Our team excels in precision balancing of crankshafts, a critical process for V-type engines to eliminate vibrations and minimize bearing stress, ensuring seamless engine performance. We meticulously design and integrate counterweights (bob weights) as a cornerstone of our manufacturing process, leveraging our deep expertise to achieve optimal balance. Adhering to international standards like ISO 1940-1 and ISO 21940-1, we utilize state-of-the-art dynamic balancing machines equipped with advanced vibration sensors to detect and correct imbalances with unparalleled accuracy. By employing techniques such as precise drilling or strategic weight addition, we guarantee smooth, reliable operation, showcasing our mastery in delivering high-performance crankshafts.
Quality Control
Quality control is vital for the crankshaft, a critical component of internal combustion engines, to ensure performance, durability, and reliability. The Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is an advanced tool used for precise dimensional and geometric inspection of the crankshaft, verifying compliance with stringent standards during the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
The crankshaft production process at Noor Powertrain Company utilizes meticulous material selection, advanced CAD design, and precision manufacturing techniques compliant with ISO standards to produce crankshafts with high accuracy, durability, and optimal performance. Rigorous quality control using tools like CMM ensures compliance with global standards. This process, combined with reverse engineering and localization, demonstrates the company’s capability to deliver advanced, competitive components in the global automotive industry, establishing Noor Powertrain as a reliable and innovative partner.
